Syllabus | Mathematics for Common University Entrance Test CUET (UG) – 2022
MATHEMATICS / APPLIED MATHEMATICS (319) | Syllabus for Class 12
Note:
There will be one Question Paper which will contain Two Sections i.e. Section A and Section B [B1 and B2].
Section A will have 15 questions covering both i.e. Mathematics/Applied Mathematics which will be compulsory for all candidates
Section B1 will have 35 questions from Mathematics out of which 25 questions need to be attempted.
Section B2 will have 35 questions purely from Applied Mathematics out of which 25 question will be
attempted
SECTION A
- Algebra
(i) Matrices and types of Matrices
(ii) Equality of Matrices, transpose of a Matrix, Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrix
(iii) Algebra of Matrices
(iv) Determinants
(v) Inverse of a Matrix
(vi) Solving of simultaneous equations using Matrix Method
- Calculus
(i) Higher order derivatives
(ii) Tangents and Normals
(iii) Increasing and Decreasing Functions
(iv). Maxima and Minima - Integration and its Applications
(i) Indefinite integrals of simple functions
(ii) Evaluation of indefinite integrals
(iii) Definite Integrals
(iv). Application of Integration as area under the curve - Differential Equations
(i) Order and degree of differential equations
(ii) Formulating and solving of differential equations with variable separable - Probability Distributions
(i) Random variables and its probability distribution
(ii) Expected value of a random variable
(iii) Variance and Standard Deviation of a random variable
(iv). Binomial Distribution - Linear Programming
(i) Mathematical formulation of Linear Programming Problem
(ii) Graphical method of solution for problems in two variables
(iii) Feasible and infeasible regions
(iv) Optimal feasible solution
Section B1: Mathematics
UNIT I: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
- Relations and Functions
Types of relations: Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto
functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations. - Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Definition, range, domain, principal value branches. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.
Elementary properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
- Matrices
Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication of matrices, simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non-commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order 2). Concept of elementary row and column operations. Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries). - Determinants
Determinant of a square matrix (upto 3×3 matrices), properties of determinants, minors, co factors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, in consistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
UNIT III: CALCULUS
- Continuity and Differentiability
Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit function. Concepts of exponential, logarithmic functions.
Derivatives of log x and ex Logarithmic differentiation. Derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second-order derivatives. Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems (without proof) and their geometric interpretations. - Applications of Derivatives
Applications of derivatives: Rate of change, increasing/decreasing functions, tangents and normals, approximation, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real-life situations). Tangent and Normal. - Integrals
Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution,by partial fractions and by parts, only simple integrals of the type –
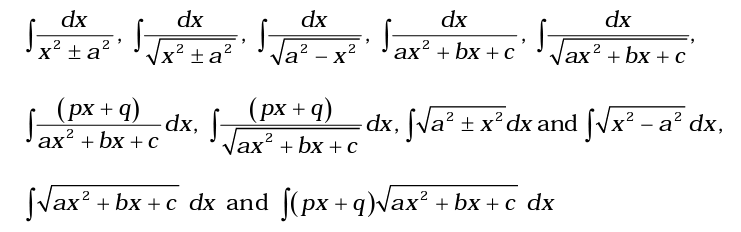
to be evaluated.
Definite integrals as a limit of a sum. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus(without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
- Applications of the Integrals
Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, arcs of circles/parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only), area between the two above said curves(the region should be clearly identifiable). - Differential Equations
Definition,order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Formation of
differential equation whose general solution is given.Solution of differential equations by method of
separation of variables, homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions
of linear differential equation of the type –
dy
— Py = Q, where P and Q are functions of x or constant
dx
dx
— Px = Q, where P and Q are functions of y or constant
dy
UNIT IV: VECTORS AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
- Vectors
Vectors and scalars,magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines/ratios of vectors.Types of vectors(equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Scalar(dot) product of vectors, projection of a vector on a line. Vector(cross) product of vectors, scalar triple product. - Three-dimensional Geometry
Direction cosines/ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. Angle between (i)two lines,(ii)two planes,(iii) a line and a plane. Distance of a point from a plane.
Unit V: Linear Programming
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints,objective function, optimization, different types of linear programming (L.P.) problems, mathematical formulation of L.P. problems, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions, feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (upto three non-trivial constrains).
Unit VI: Probability
Multiplications theorem on probability. Conditional probability, independent events, total probability, Baye’s theorem. Random variable and its probability distribution,mean and variance of haphazard variable. Repeated independent (Bernoulli) trials and Binomial distribution.
.
Section B2: Applied Mathematics
- Unit I: Numbers, Quantification and Numerical Applications
- A. Modulo Arithmetic
- Define modulus of an integer
- Apply arithmetic operations using modular arithmetic rules
- B. Congruence Modulo
- Define congruence modulo
- Apply the definition in various problems
- C. Allegation and Mixture
- Understand the rule of allegation to produce a mixture at a given price
- Determine the mean price of a mixture
- Apply rule of allegation
- D. Numerical Problems
- Solve real life problems mathematically
- E. Boats and Streams
- Distinguish between upstream and downstream
- Express the problem in the form of an equation
- F. Pipes and Cisterns
- Determine the time taken by two or more pipes to fill or
- G. Races and Games
- Compare the performance of two players w.r.t. time, distance taken/distance covered/ Work done from the given data
- H. Partnership
- Differentiate between active partner and sleeping partner
- Determine the gain or loss to be divided among the partners in the ratio of their investment with due consideration of the time volume/surface area for solid formed using two or more shapes
- I. Numerical Inequalities
- Describe the basic concepts of numerical inequalities
- Understand and write numericaline qualities
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
- A. Matrices and types of matrices
- Define matrix
- Identify different kinds of matrices
- B. Equality of matrices, Transpose of a matrix, Symmetric and Skew symmetric matrix
- Determine equality of two matrices
- Write transpose of given matrix
- Define symmetric and skew symmetric matrix
UNIT III: CALCULUS
- A. Higher Order Derivatives
- Determine second and higher order derivatives
- Understand differentiation of parametric functions and implicit functions Identify dependent and independent variables
- B. Marginal Cost and Marginal Revenue using derivatives
- Define marginal cost and marginal revenue
- Find marginal cost and marginal revenue
- C. Maxima and Minima
- Determine critical points of the function
- Find the point(s) of local maxima and local minima and corresponding local maximum and local minimum values
- Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum value of a function
UNIT IV: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
- A. Probability Distribution
- Understand the concept of Random Variables and its Probability Distributions
- Find probability distribution of discrete random variable
- B. Mathematical Expectation
- Apply arithmetic mean of frequency distribution to find the expected value of a random variable
- C. Variance
- Calculate the Variance and S.D.of a random variable
UNIT V: INDEX NUMBERS AND TIME BASED DATA
- A. Index Numbers
- Define Index numbers as aspecial type of average
- B. Construction ofIndex numbers
- Construct different type of indexnumbers
- C. Test of Adequacy of Index Numbers
- Apply time reversal test
UNIT VI: UNIT V: INDEX NUMBERS AND TIME BASED DATA
- A. Population andSample
- Define Population and Sample
- Differentiate between population and sample
- Define a representative sample from a population
- B. Parameter and Statistics and Statistical Interferences
- Define Parameter with reference to Population
- Define Statistics with reference to Sample
- Explain the relation between Parameter and Statistic
- Explain the limitation of Statistic to generalize the estimation for population
- Interpret the concept of Statistical Significance and Statistical Inferences
- State Central Limit Theorem
- Explain the relation between Population-Sampling Distribution-Sample
UNIT VII: INDEX NUMBERS AND TIME-BASED DATA
- A. Time Series
- Identify time series as chronological data
- B. Components of Time Series
- Distinguish between different components of time series
- C. Time Series analysis for univariate data
- Solve practical problems based on statistical data and Interpret
UNIT VIII: FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS
- A. Perpetuity, Sinking Funds
- Explain the concept of perpetuity and sinking fund
- Calculate perpetuity
- Differentiate between sinking fund and saving account
- B. Valuation of Bonds
- Define the concept of valuation of bond and related terms
- Calculate value of bond using present value approach
- C. Calculation of EMI
- Explain the concept of EMI
- Calculate EMI using various methods
- D. Linear method of Depreciation
- Define the concept of linear method of Depreciation
- Interpret cost, residual value and useful life of an asset from the given information
- Calculate depreciation
UNIT IX: LINEAR PROGRAMMING
- A. Introduction and related terminology
- Familiarize with terms related to Linear Programming Problem
- B. Mathematical formulation of Linear Programming Problem
- Formulate Linear Programming Problem
- C. Different types of Linear Programming Problems
- Identify and formulate different types of LPP
- D. Graphical Method of Solution for problems in two Variables
- Draw the Graph for a system of linear inequalities involving two variables and to find its solution graphically
- E. Feasible and Infeasible Regions
- Identify feasible, infeasible and bounded regions
- F. Feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solution
- Understand feasible and infeasible solutions
- Find optimal feasible solution